瀏覽量: 165
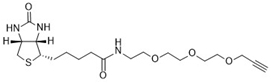
- 產(chǎn)品名稱(chēng): Biotin Alkyne
- 產(chǎn)品貨號(hào): CSC303
- 貨期: 現(xiàn)貨
- 價(jià)格與訂購(gòu): 900
- 數(shù)量:
庫(kù)存: 10
- 規(guī)格: 5mg
- 產(chǎn)品信息
- 如何訂購(gòu)
Introduction
Click chemistry describes a class of chemical reactions that use bio-orthogonal or biologically unique moieties to label and detect a molecule of interest in mild, aqueous conditions. The click reaction involves a copper-catalyzed triazole formation from an azide and an alkyne. The azide and alkyne moieties can be used interchangeably; either one can be used to tag the molecule of interest, while the other is used for subsequent detection.
The biotin alkyne is reactive with azide via a copper-catalyzed click reaction. Biotin can be subsequently detected with streptavidin, avidin or NeutrAvidin? biotin-binding protein.
Features
Efficiency—the click reaction is complete in less than 1 hour;
Specificity—the reaction between the label and detection tag is selective and specific;
Stability—the reaction product contains an irreversible, covalent bond;
Biologically inert—the components of the reaction do not undergo any side reactions.
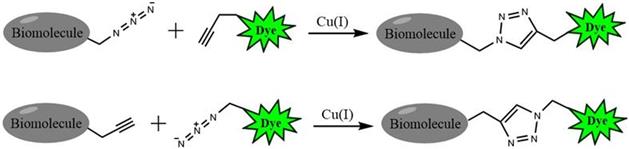
Figure 1. Click chemistry labeling
Specifications
Label
Biotin
Ex/Em
–
Detection Method
–
Solubility
DMSO, DMF
Molecular Weight
413.53
Product Size
5 mg
Storage Conditions
-20 ℃, protect from light
Shipping Condition
Room Temperature
Reference
1.Direct in-gel fluorescence detection and cellular imaging of O-GlcNAc-modified proteins.
Clark PM, Dweck JF, Mason DE, Hart CR, Buck SB, Peters EC, Agnew BJ, Hsieh-Wilson LC,J Am Chem Soc (2008) 130:11576-11577
2.Robust fluorescent detection of protein fatty-acylation with chemical reporters.
Charron G, Zhang MM, Yount JS, Wilson J, Raghavan AS, Shamir E, Hang HC,J Am Chem Soc (2009) 131:4967-4975
3.Regulation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase IV by O-GlcNAc modification.
Dias WB, Cheung WD, Wang Z, Hart GW,J Biol Chem (2009) 284:21327-21337
Note
For research use only .
上一篇 Biotin Azide
Cy5 Azide 下一篇

 地 址:
地 址: 產(chǎn)品銷(xiāo)售:
產(chǎn)品銷(xiāo)售: E - mail :
E - mail : 郵 編:
郵 編:
 Amily
Amily